User Guide
Contents
Notice
The Total Compute 2022 (TC2) software stack uses bash scripts to build a Board Support Package (BSP) and a choice of three possible distributions including Buildroot, Debian or Android.
Prerequisites
- These instructions assume that:
Your host PC is running Ubuntu Linux 20.04;
You are running the provided scripts in a
bashshell environment;This release requires TC2 Fast Model platform (FVP) version 11.22.34.
To get the latest repo tool from Google, please run the following commands:
mkdir -p ~/bin
curl https://storage.googleapis.com/git-repo-downloads/repo > ~/bin/repo
chmod a+x ~/bin/repo
export PATH=~/bin:$PATH
- To build and run Android, the minimum requirements for the host machine can be found at https://source.android.com/setup/build/requirements. These include:
at least 250 GB of free disk space to check out the code and an extra 150 GB to build it. If you conduct multiple builds, you need additional space;
at least 32 GB of available RAM/swap.
To avoid errors while attempting to clone/fetch the different TC software components, your system should have a proper minimum git config configuration. The following command exemplifies the typical git config configuration required:
git config --global user.name "<user name>"
git config --global user.email "<email>"
git config --global protocol.version 2
To install and allow access to docker, please run the following commands:
sudo apt install docker.io
# ensure docker service is properly started and running
sudo systemctl restart docker
sudo chmod 777 /var/run/docker.sock
To manage Docker as a non-root user, please run the following commands:
sudo groupadd docker
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
newgrp docker
Download the source code and build
- The TC2 software stack supports the following distros:
Buildroot (a minimal distro containing Busybox);
Debian (based on Debian 12 Bookworm);
Android (based on Android 13).
Download the source code
Create a new folder that will be your workspace, which will henceforth be referred to as <TC2_WORKSPACE>
in these instructions.
mkdir <TC2_WORKSPACE>
cd <TC2_WORKSPACE>
export TC2_RELEASE=refs/tags/TC2-2023.08.15
To sync Buildroot or Debian source code, please run the following repo commands:
repo init -u https://gitlab.arm.com/arm-reference-solutions/arm-reference-solutions-manifest \
-m tc2.xml \
-b ${TC2_RELEASE} \
-g bsp
repo sync -j `nproc` --fetch-submodules
To sync Android source code, please run the following repo commands:
repo init -u https://gitlab.arm.com/arm-reference-solutions/arm-reference-solutions-manifest \
-m tc2.xml \
-b ${TC2_RELEASE} \
-g android
repo sync -j `nproc` --fetch-submodules
Warning
Synchronization of the Android code from Google servers may fail due to connection problems and/or to an enforced rate limit related with the maximum number of concurrent fetching jobs. The previous commands assume that the maximum number of jobs concurrently fetching code will be a perfect match of the number of CPU cores available, which should work fine most of the time. If experiencing constant errors on consecutive fetch code attempts, please do consider deleting your entire workspace (which will ensure a clean of the support .repo folder containing the previously partial fetched files), by running the command cd .. ; rm -rf <TC2_WORKSPACE> and repeat the previous commands listed in this section to recreate the workspace (optionally, also reducing the number of jobs, for example to a maximum of 6, by adopting the following command repo sync -j 6 --fetch-submodules).
- Once the previous process finishes, the current
<TC2_WORKSPACE>should have the following structure: build-scripts/: the components build scripts;run-scripts/: scripts to run the FVP;src/: each component’s git repository.
Initial Setup
- The setup includes two parts:
setup a docker image;
setup the environment to build TC images.
Setting up a docker image involves pulling the prebuilt docker image from a docker registry. If that fails, it will build a local docker image.
To setup a docker image, patch the components, install the toolchains and build tools, please run the commands mentioned in the following Build variants configuration section, according to the distro and variant of interest.
The various tools will be installed in the <TC2_WORKSPACE>/tools/ directory.
Build options
Debian OS build variant
Currently, the Debian OS build distro does not support software or hardware rendering. Considering this limitation, this build variant should be only used for development or validation work that does not imply pixel rendering.
Android OS build variants
Note
Android based stack takes considerable time to build, so start the build and go grab a cup of coffee!
Hardware vs Software rendering
The Android OS based build distro supports the following variants regarding the use of the GPU rendering:
TC_GPU value |
Description |
|---|---|
swr |
Android display with Swiftshader (software rendering) |
hwr |
Mali GPU (hardware rendering based on DDK source code - please see below note) |
hwr-prebuilt |
Mali GPU (hardware rendering based on prebuilt binaries) |
Note
GPU DDK source code is available only to licensee partners (please contact support@arm.com).
Android Verified Boot (AVB) with/without authentication
The Android images can be built with or without authentication enabled using Android Verified Boot (AVB) through the use of the -a option.
AVB build is done in userdebug mode and takes a longer time to boot as the images are verified.
This option does not influence the way the system boots, rather it adds an optional sanity check on the prerequisite images.
Build variants configuration
This section provides a quick guide on how to build the different TC build variants using the most common options.
Buildroot build
To build the Buildroot distro, please run the following commands:
export PLATFORM=tc2
export FILESYSTEM=buildroot
export TC_TARGET_FLAVOR=fvp
cd build-scripts
./setup.sh
Debian build
Currently, the Debian build does not support software or hardware rendering. As such, the TC_GPU variable value should not be defined. The Debian build can still be a valuable resource when just considering other types of development or validation work, which do not involve pixel rendering.
Debian build (without software or GPU hardware rendering support)
To build the Debian distro, please run the following commands:
export PLATFORM=tc2
export FILESYSTEM=debian
export TC_TARGET_FLAVOR=fvp
cd build-scripts
./setup.sh
Android build
To build Android with Android Verified Boot (AVB) enabled, please run the next command to enable the corresponding flag in addition to any of the following Android command variants (please note that this needs to be run before running ./setup.sh):
export AVB=true
Android can be built with or without GPU hardware rendering support by setting the TC_GPU environment variable accordingly, as described in the following command usage examples.
Android build with hardware rendering support based on prebuilt binaries
To build the Android distro with hardware rendering based on prebuilt binaries, please run the following commands:
export PLATFORM=tc2
export FILESYSTEM=android-fvp
export TC_GPU=hwr-prebuilt
export TC_TARGET_FLAVOR=fvp
cd build-scripts
./setup.sh
Android build with hardware rendering support based on DDK source code
To build the Android distro with hardware rendering based on DDK source code, please run the following commands:
export PLATFORM=tc2
export FILESYSTEM=android-fvp
export TC_GPU=hwr
export TC_TARGET_FLAVOR=fvp
export GPU_DDK_REPO=<PATH TO GPU DDK SOURCE CODE>
export GPU_DDK_VERSION="releases/r41p0_01eac0"
export LM_LICENSE_FILE=<LICENSE FILE>
export ARMLMD_LICENSE_FILE=<LICENSE FILE>
export ARMCLANG_TOOL=<PATH TO ARMCLANG TOOLCHAIN>
cd build-scripts
./setup.sh
Note
GPU DDK source code is available only to licensee partners (please contact support@arm.com).
Android build with software rendering support
To build the Android distro with software rendering, please run the following commands:
export PLATFORM=tc2
export TC_GPU=swr
export TC_TARGET_FLAVOR=fvp
export FILESYSTEM=android-fvp
cd build-scripts
./setup.sh
Warning
If building the TC2 software stack for more than one target, please ensure you run a clean build between each different build to avoid setup/building errors (refer to the next section “More about the build system” for command usage examples on how to do this).
Warning
If running repo sync again is needed at some point, then the setup.sh script also needs to be run again, as repo sync can discard the patches.
Note
Most builds will be done in parallel using all the available cores by default. To change this number, run export PARALLELISM=<number of cores>
Build command
To build the whole TC2 software stack for any of the supported distros, simply run:
./run_docker.sh ./build-all.sh build
- Once the previous process finishes, the previously defined environment variable
$FILESYSTEMwill be automatically used and the current<TC2_WORKSPACE>should have the following structure: build files are stored in
<TC2_WORKSPACE>/output/<$FILESYSTEM>/tmp_build/;final images will be placed in
<TC2_WORKSPACE>/output/<$FILESYSTEM>/deploy/.
More about the build system
The build-all.sh script will build all the components, but each component has its own script, allowing it to be built, cleaned and deployed separately.
All scripts support the build, clean, deploy, patch commands. build-all.sh also supports all, which performs a clean followed by a rebuild of all the stack.
For example, to build, deploy, and clean SCP, run:
./run_docker.sh ./build-scp.sh build
./run_docker.sh ./build-scp.sh deploy
./run_docker.sh ./build-scp.sh clean
The platform and filesystem used should be defined as described previously, but they can also be specified as the following example:
./run_docker.sh ./build-all.sh \
-p $PLATFORM \
-f $FILESYSTEM \
-t $TC_TARGET_FLAVOR \
-g $TC_GPU build
Build Components and its dependencies
A new dependency to a component can be added in the form of $component=$dependency in the dependencies.txt file
To build a component and rebuild those components that depend on it, run:
./run_docker.sh ./$filename build with_reqs
Those options work for all the build-*.sh scripts.
Provided components
Firmware Components
Trusted Firmware-A
Based on Trusted Firmware-A
Script |
<TC2_WORKSPACE>/build-scripts/build-tfa.sh |
Files |
|
System Control Processor (SCP)
Based on SCP Firmware
Script |
<TC2_WORKSPACE>/build-scripts/build-scp.sh |
Files |
|
U-Boot
Based on U-Boot
Script |
<TC2_WORKSPACE>/build-scripts/build-u-boot.sh |
Files |
|
Hafnium
Based on Hafnium
Script |
<TC2_WORKSPACE>/build-scripts/build-hafnium.sh |
Files |
|
OP-TEE
Based on OP-TEE
Script |
<TC2_WORKSPACE>/build-scripts/build-optee-os.sh |
Files |
|
S-EL0 trusted-services
Based on Trusted Services
Script |
<TC2_WORKSPACE>/build-scripts/build-trusted-services.sh |
Files |
|
Linux
The component responsible for building a 5.15 version of the Android Common kernel (ACK).
Script |
<TC2_WORKSPACE>/build-scripts/build-linux.sh |
Files |
|
Trusty
Based on Trusty
Script |
<TC2_WORKSPACE>/build-scripts/build-trusty.sh |
Files |
|
Distributions
Buildroot Linux distro
The layer is based on the Buildroot Linux distribution.
The provided distribution is based on BusyBox and built using glibc.
Script |
<TC2_WORKSPACE>/build-scripts/build-buildroot.sh |
Files |
|
Debian Linux distro
Script |
<TC2_WORKSPACE>/build-scripts/build-debian.sh |
Files |
|
Android
Script |
<TC2_WORKSPACE>/build-scripts/build-android.sh |
Files |
|
Run scripts
Within the <TC2_WORKSPACE>/run-scripts/ there are several convenience functions for testing the software
stack. Usage descriptions for the various scripts are provided in the following sections.
Obtaining the TC2 FVP
The TC2 FVP is available to partners to build and run on Linux host environments.
To download the latest publicly available TC2 FVP model, please visit the Arm Ecosystem FVP downloads webpage or contact Arm (support@arm.com).
Running the software on FVP
A Fixed Virtual Platform (FVP) of the TC2 platform must be available to run the included run scripts.
The run-scripts structure is as follows:
run-scripts
|--tc2
|--run_model.sh
|-- ...
Ensure that all dependencies are met by running the FVP: ./path/to/FVP_TC2. You should see
the FVP launch, presenting a graphical interface showing information about the current state of the FVP.
The run_model.sh script in <TC2_WORKSPACE>/run-scripts/tc2 will launch the FVP, providing
the previously built images as arguments. Run the ./run_model.sh script:
./run_model.sh
Incorrect script use, call script as:
<path_to_run_model.sh> [OPTIONS]
OPTIONS:
-m, --model path to model
-d, --distro distro version, values supported [buildroot, android-fvp, debian]
-a, --avb [OPTIONAL] avb boot, values supported [true, false], DEFAULT: false
-t, --tap-interface [OPTIONAL] enable TAP interface
-n, --networking [OPTIONAL] networking, values supported [user, tap, none]
DEFAULT: tap if tap interface provided, otherwise user
-- [OPTIONAL] After -- pass all further options directly to the model
Running Buildroot
./run-scripts/tc2/run_model.sh -m <model binary path> -d buildroot
Running Debian
./run-scripts/tc2/run_model.sh -m <model binary path> -d debian
Running Android
Android general common run command
The following command is common to Android builds with AVB disabled, software or any of the hardware rendering variants. To run any of the mentioned Android variants, please run the following command:
./run-scripts/tc2/run_model.sh -m <model binary path> -d android-fvp
Android with AVB enabled
To run Android with AVB enabled, please run the following command:
./run-scripts/tc2/run_model.sh -m <model binary path> -d android-fvp -a true
Expected behaviour
- When the script is run, four terminal instances will be launched:
terminal_uart_apused by the non-secure world components U-boot, Linux Kernel and filesystem (Buildroot/Debian/Android);terminal_uart1_apused by the secure world components TF-A, Hafnium, Trusty and OP-TEE;terminal_s0used for the SCP logs;terminal_s1used by RSS logs (no output by default).
Once the FVP is running, the hardware Root of Trust will verify AP and SCP images, initialize various crypto services and then handover execution to the SCP. SCP will bring the AP out of reset. The AP will start booting from its ROM and then proceed to boot Trusted Firmware-A, Hafnium, Secure Partitions (OP-TEE, Trusted Services in Buildroot and Trusty in Android) then U-Boot, and finally the corresponding Linux Kernel distro.
When booting Buildroot or Debian, the model will boot the Linux kernel and present a login prompt on the terminal_uart_ap window. Login
using the username root and the password root (password is only required for Debian). You may need to hit Enter for the prompt to appear.
When booting Android, the GUI window Fast Models - Total Compute 2 DP0 shows the Android logo and on boot completion,
the window will show the typical Android home screen.
Running sanity tests
This section provides information on some of the suggested sanity tests that can be executed to exercise and validate the TC Software stack functionality, as well as information regarding the expected behaviour and test results.
Note
The information presented for any of the sanity tests described in this section should NOT be considered as indicative of hardware performance. These tests and the FVP model are only intended to validate the functional flow and behaviour for each of the features.
Validate the TensorFlow Lite ML flow
A typical Machine Learning (ML) inference flow can be validated using the TensorFlow Lite’s model benchmarking application.
This application can consume any TensorFlow Lite neural network model file and run a user specified number of inferences on it, allowing to benchmark performance for the whole graph and for individual operators.
More information on the Model Benchmark tool can be found here.
Prerequisites
- For this test, two files will be required:
benchmark_modelbinary: this file is part of the TC build and is automatically built when targeting Buildroot;<any model>.tflitemodel: there is no requirement for a specific model file as long as it is specified in a valid.tfliteformat; for the simplicity of just running a sanity test, two models are provided with the build and are automatically integrated into the distro filesystem (being located at/opt/arm/ml).
Running the provided TensorFlow Lite ML model examples
The following command describes how to run the benchmark_model application to profile the “Mobile Object Localizer” TensorFlow Lite model, which is one of the provided TensorFlow Lite ML model examples.
Although the command arguments are expected to greatly vary according to different use cases and models, this example provides the typical command usage skeleton for most of the models.
More information on the Model Benchmark Tool and command usage examples can be found here.
To run the benchmark_model to profile the “Mobile Object Localizer” model, please follow the following steps:
using
terminal_uart_ap, login to the device/FVP model running TC and run the following commands:# the following command ensures correct path location to load the provided example ML models cd /opt/arm/ml benchmark_model --graph=mobile_object_localizer_v1.tflite \ --num_threads=4 --num_runs=1 --min_secs=0.01
The benchmark model application will run profiling the Mobile Object Localizer model and after a few seconds, some statistics and execution info will be presented on the terminal.
Note
This test is specific to Buildroot.
Manually uploading a TensorFlow Lite ML model
There may be situations where the developer wishes to use their own TensorFlow Lite model.
This section describes the steps necessary to manually upload a model to the running TC FVP model and run it.
To the purpose of demonstrating this process, an old MobileNet Graph model version will be taken as example (the model can be downloaded from here).
To run the benchmark_model application and profile the “MobileNet Graph” model, please proceed as described:
start by downloading and decompressing the MobileNet graph model to your local host machine using the following command:
# any host path location can be used (as long it has writable permissions) mkdir MobileNetGraphTFModel && cd MobileNetGraphTFModel wget https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/models/tflite/mobilenet_v1_224_android_quant_2017_11_08.zip unzip mobilenet_v1_224_android_quant_2017_11_08.zipupload the MobileNet Graph model to the TC FVP model using the following command:
# the following command assumes that the port 8022 is being used as specified in the run_model.sh script scp -P 8022 mobilenet_quant_v1_224.tflite root@localhost:/opt/arm/ml/ # password (if required): rootonce the model has been uploaded to the remote TC FVP model, the
benchmark_modelcan be run as described previously in theRunning the provided TensorFlow Lite ML model examplessection.
OP-TEE
For OP-TEE, the TEE sanity test suite can be run using command xtest on the terminal_uart_ap.
Please be aware that this test suite will take some time to run all its related tests.
Note
This test is specific to Buildroot only. An example of the expected test result for this test is illustrated in the related Total Compute Platform Expected Test Results document section.
Trusted Services and Client application
For Trusted Services, please run the command ts-service-test -sg ItsServiceTests -sg PsaCryptoApiTests -sg CryptoServicePackedcTests -sg CryptoServiceProtobufTests -sg CryptoServiceLimitTests -v for Service API level tests, and run ts-demo for the demonstration of the client application.
Note
This test is specific to Buildroot only. An example of the expected test result for this test is illustrated in the related Total Compute Platform Expected Results document section.
Trusty
On the Android distribution, Trusty provides a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE).
The functionality of Trusty IPC can be tested using the command tipc-test -t ta2ta-ipc with root privilege
(once Android boots to prompt, run su 0 for root access).
Note
This test is specific to Android only. An example of the expected test result for this test is illustrated in the Total Compute Platform Expected Test Results document section.
Microdroid demo
On the Android distribution, Virtualization service provides support to run Microdroid based pVM (Protected VM). For running a demo Microdroid, boot TC FVP with Android distribution. Once the Android is completely up, please run the following commands:
export ANDROID_PRODUCT_OUT=<TC2_WORKSPACE>/src/android/out/target/product/tc_fvp/
./run-scripts/tc2/run_microdroid_demo.sh
Note
This test is specific to Android only. An example of the expected test result for this test is illustrated in the related Total Compute Platform Expected Test Results document section.
Kernel Selftest
Tests are located at /usr/bin/selftest on the device.
To run all the tests in one go, use ./run_kselftest.sh script. Tests can also be run individually.
./run_kselftest.sh --summary
Warning
KSM driver is not a part of the TC2 kernel. Hence, one of the MTE Kselftests will fail for the check_ksm_options test.
Note
This test is specific to Buildroot only. An example of the expected test result for this test is illustrated in the related Total Compute Platform Expected Test Results document section.
MPAM
The hardware and the software requirements required for the MPAM feature can be verified by running the command testing_mpam.sh on terminal_uart_ap (this script is located inside the /bin folder, which is part of the default $PATH environment variable, allowing this command to be executed from any location in the device filesystem).
Note
This test is specific to Buildroot only. An example of the expected test result for this test is illustrated in the related Total Compute Platform Expected Test Results document section.
MPMM
Note
The following two tests require to execute the FVP-model enforcing the additional load of the ScalableVectorExtension.so plugin (which is provided and part of your FVP bundle). The following command demonstrates the typical command skeleton required to execute the fvp-model in this situation:
./run-scripts/tc2/run_model.sh -m <fvp-model binary path> -d buildroot \
-- \
--plugin <fvp-model plugin path/ScalableVectorExtension.so>
- The functionality of the MPMM module in the SCP firmware can be leveraged to:
set the proper gear for each core based on the workload. This functionality can be verified by checking the
INFOlevel SCP logs while executing thevector_workloadtest application on theterminal_uart_apwindow as follows:
vector_workloadenforce the maximum clock frequency for a group of cores of the same type, based on the current gear set for each core in that group. This functionality can be exercised by running the provided shell script
test_mpmm.shwhich will runvector_workloadon the different cores. This test ensures that the maximum clock frequency for a group of cores of the same type does not exceed the values set in Perf Constraint Lookup Table (PCT) of the MPMM module in the SCP firmware.
To run this test, please run the following command in the
terminal_uart_apwindow:test_mpmm.sh fvp
Note
These tests are specific to Buildroot only. An example of the expected test result for the second test is illustrated in the related Total Compute Platform Expected Test Results document section.
BTI
On the terminal_uart_ap run:
cd /data/nativetest64/bti-unit-tests/
./bti-unit-tests
Note
This test is specific to Android builds. An example of the expected test result for this test is illustrated in the related Total Compute Platform Expected Test Results document section.
MTE
On the terminal_uart_ap run:
su
cd /data/nativetest64/mte-unit-tests/
./mte-unit-tests
Note
This test is specific to Android builds. An example of the expected test result for this test is illustrated in the related Total Compute Platform Expected Test Results document section.
PAUTH
On the terminal_uart_ap run:
su
cd /data/nativetest64/pauth-unit-tests/
./pauth-unit-tests
Note
This test is specific to Android builds. An example of the expected test result for this test is illustrated in the related Total Compute Platform Expected Test Results document section.
EAS with LISA
This test requires Lisa to be installed. Please refer to the LISA documentation to get more information about the requirements, dependencies and installation process of LISA on your system.
To setup Lisa, please run the following commands:
git clone --depth=1 --branch=v3.1.0 https://github.com/ARM-software/lisa.git
cd lisa
sudo ./install_base.sh --install-all
The following commands should be run each time LISA is run:
source init_env
export TC_WORKSPACE=<TC2_WORKSPACE>
export FILESYSTEM=buildroot
For FVP with buildroot, boot the FVP model to buildroot as you normally would, making sure user networking is enabled:
exekall run lisa.tests.scheduler.eas_behaviour --conf <path to target_conf_linux.yml>
The following excerpt illustrates the contents of the target_conf_buildroot.yml file:
target-conf:
kind: linux
name: tc
host: localhost
port: 8022
username: root
password: ""
strict-host-check: false
kernel:
src: ${TC_WORKSPACE}/output/${FILESYSTEM}/tmp_build/linux
modules:
make-variables:
CC: clang
build-env: alpine
wait-boot:
enable: false
devlib:
file-xfer: scp
max-async: 1
Note
This test is specific to Buildroot only. An example of the expected test result for this test is illustrated in the related Total Compute Platform Expected Test Results document section.
CPU hardware capabilities
The Buildroot build variant provides a script that allows to validate the advertisement for the FEAT_AFP, FEAT_ECV and FEAT_WFxT CPU hardware capabilities.
On the terminal_uart_ap run:
test_feats_arch.sh
Note
This test is specific to Buildroot only. An example of the expected test result for this test is illustrated in the related Total Compute Platform Expected Test Results document section.
Debugging on Arm Development Studio
This section describes the steps to debug the TC software stack using Arm Development Studio.
Attach and Debug
Build the target with debug enabled (the file
<TC2_WORKSPACE>/build-scripts/configcan be configured to enable debug);Run the distro as described in the section
Running the software on FVPwith the extra parameters-- -Ito attach to the debugger. The full command should look like the following:./run-scripts/tc2/run_model.sh -m <model binary path> -d <distro> -- -I
Select the target
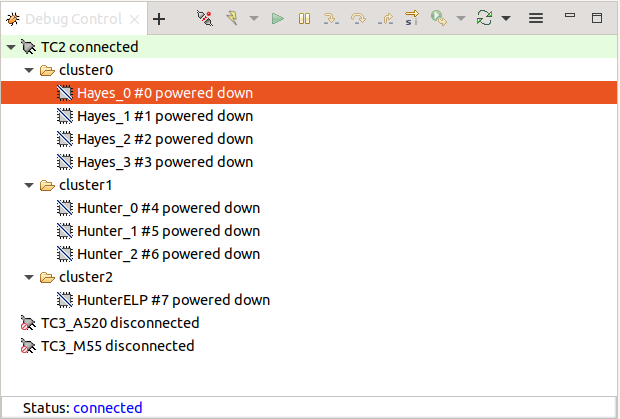
Arm FVP -> TC2 -> Bare Metal Debug -> Hayesx4/Hunterx3/HunterELP SMPAfter connection, use options in debug control console (highlighted in the below diagram) or the keyboard shortcuts to
step,runorhalt.To add debug symbols, right click on target ->
Debug configurationsand underfilestab add path toelffiles.Debug options such as
break points,variable watch,memory viewand so on can be used.
Note
This configuration requires Arm DS version 2023.a or later. The names of the cores shown are based on codenames instead of product names. The mapping for the actual names follows the below described convention:
Codename
Product name
Hayes
Cortex A520
Hunter
Cortex A720
Hunter ELP
Cortex X4
Switch between SCP and AP
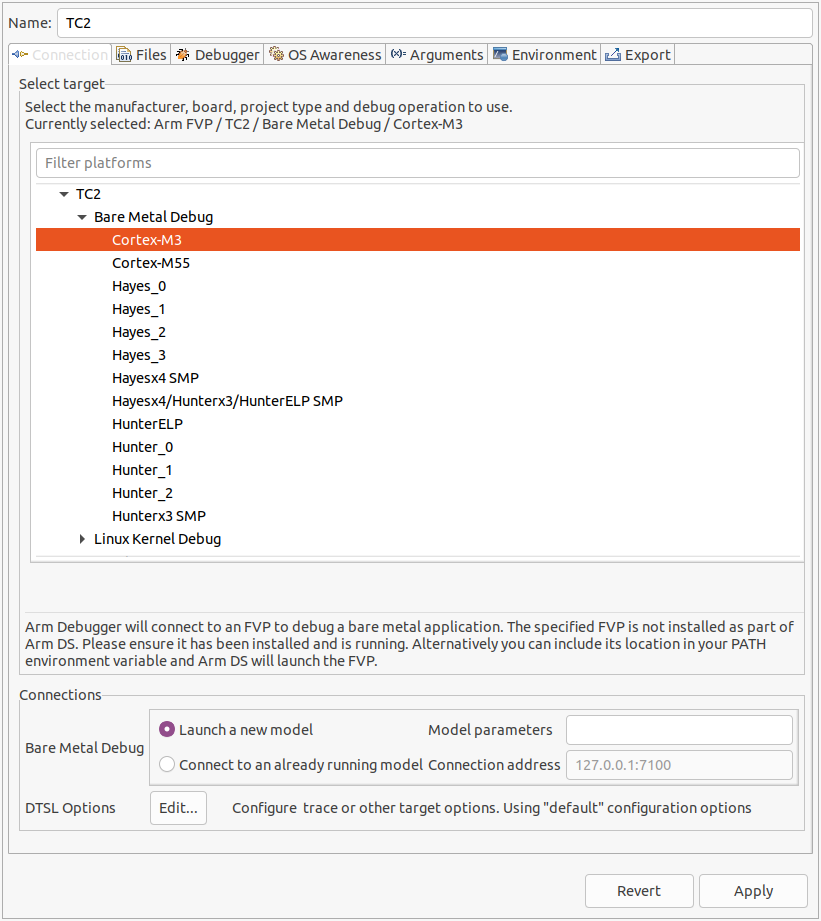
Right click on target and select
Debug Configurations;Under
Connection, selectCortex-M3for SCP or any of the remaining targets to attach to a specific AP (please refer to the previous note regarding the matching between the used codenames and actual product names);Press the
Debugbutton to confirm and start your debug session.
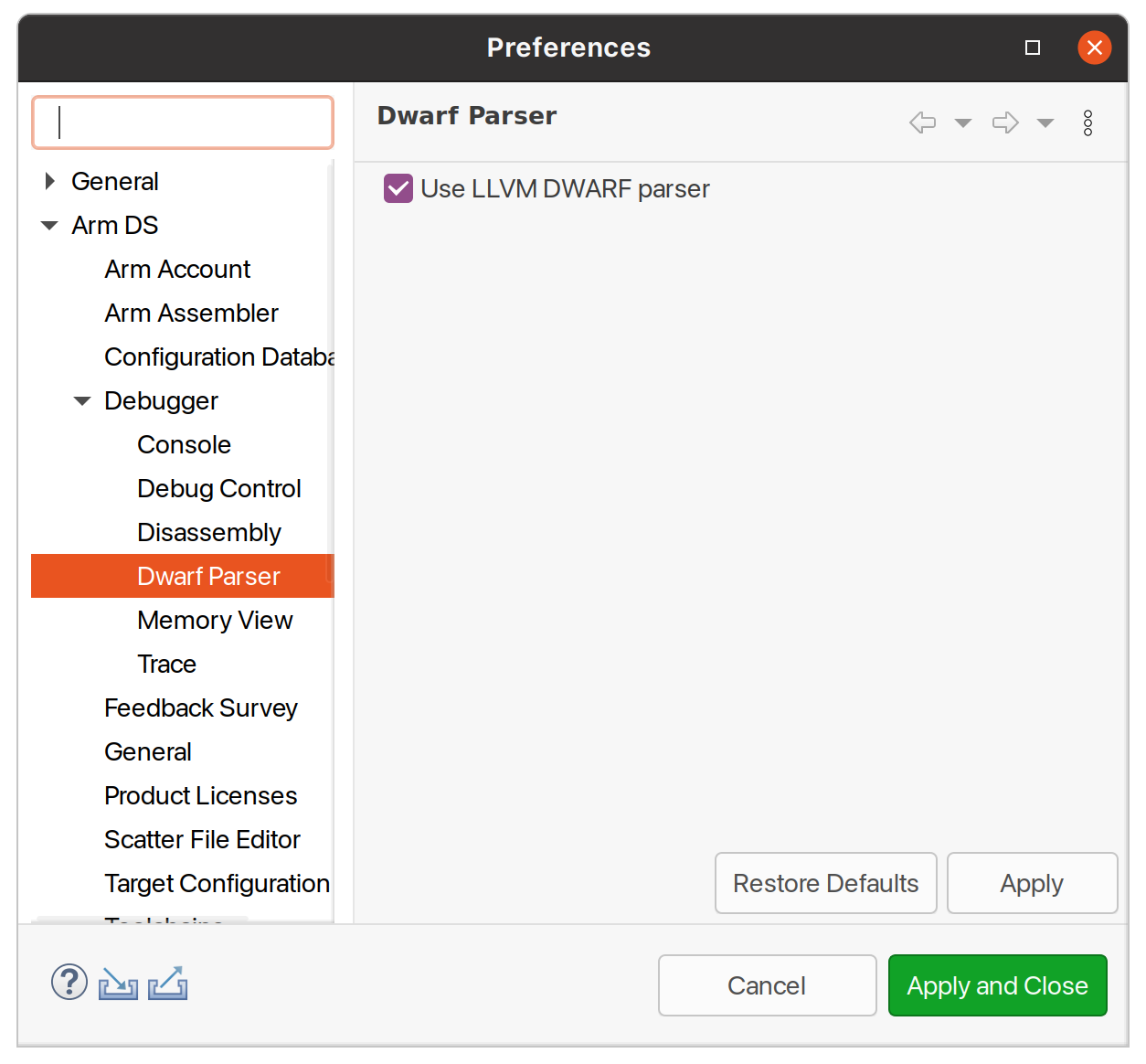
Enable LLVM parser (for Dwarf5 support)
To enable LLVM parser (with Dwarf5 support), please follow the next steps:
Select
Window->Preferences->Arm DS->Debugger->Dwarf Parser;Tick the
Use LLVM DWARF parseroption;Click the
Apply and Closebutton.
Arm DS version
The previous steps apply to the following Arm DS Platinum version/build:
Note
Arm DS Platinum is only available to licensee partners. Please contact Arm to have access (support@arm.com).
Feature Guide
Firmware Update
Currently, the firmware update functionality is only supported with the buildroot distro.
Creating Capsule
Firmware Update in the total compute platform uses the capsule update mechanism. Hence, the Firmware Image Package (FIP) binary
has to be converted to a capsule. This can be done with GenerateCapsule which is present in BaseTools/BinWrappers/PosixLike
of the edk2 project.
To generate the capsule from the fip binary, run the following command:
./GenerateCapsule -e -o efi_capsule \
--fw-version 1 \
--lsv 0 \
--guid 0d5c011f-0776-5b38-8e81-36fbdf6743e2 \
--update-image-index 0 \
--verbose fip-tc.bin
- Command argument’s explanation:
fip-tc.binis the input fip file that has the firmware binaries of the total compute platform;efi_capsuleis the name of capsule to be generated;0d5c011f-0776-5b38-8e81-36fbdf6743e2is the image type UUID for the FIP image.
Loading Capsule
The capsule generated using the above steps has to be loaded into memory during the execution of the model by providing the below FVP arguments:
--data board.dram=<location of capsule>/efi_capsule@0x2000000
This will load the capsule to be updated at address 0x82000000.
The final command to run the model for buildroot should look like the following:
./run-scripts/tc2/run_model.sh -m <model binary path> -d buildroot \
-- \
--data board.dram=<location of capsule>/efi_capsule@0x2000000
Updating Firmware
During the normal boot of the platform, stop at the U-Boot prompt and execute the following command:
TOTAL_COMPUTE# efidebug capsule update -v 0x82000000
This will update the firmware. After it is completed, reboot the platform using the FVP GUI.
AutoFDO in Android
Feedback Directed Optimization (FDO), also known as Profile Guided Optimization (PGO), uses the profile of a program’s execution to guide the optimizations performed by the compiler.
More information about the AutoFDO process in ARM can be found here.
Prerequisites
To make use of this feature, the following two requisites should be observed:
the application must be compiled to include sufficient debug information to map instructions back to source lines. For
clang/llvm, this translates into adding the-fdebug-info-for-profilingand-gline-tables-onlycompiler options;simpleperfwill identify the active program or library using the build identifier stored in the elf file. This requires the use of the following compiler flag-Wl,--build-id=sha1to be added during link time.
The following example demonstrates how to compile a sample C program named program.c using clang and observing these two prerequisites:
clang --fdebug-info-for-profiling -gline-tables-only -Wl,--build-id=sha1 program.c -o program
Steps to use AutoFDO
The following steps describe how to upload the resulting program binary object to the fvp-model, how to generate and convert the execution trace into source level profiles, and how to download and reuse that to optimize the next compiler builds:
connect to the fvp-model running instance;
Please refer to the ADB - Connect to the running FVP-model instance section for more info how to do this.
upload the previous resulting
programbinary object to the remote/usr/binpath location;Please refer to the ADB - Upload a file section for more info how to do this.
using the
terminal_uart_apwindow, navigate into/storage/selfpath location and elevate your privilege level toroot(required and crucial for next steps). This can be achieved by running the following commands on the specified terminal window:cd /storage/self su
record the execution trace of the program;
The
simpleperfapplication in Android is used to record the execution trace of the application. This trace will be captured by collecting thecs_etmevent fromsimpleperfand will be stored in aperf.datafile.The following command demonstrates how to make use of the
simpleperfapplication to record the execution trace of theprogramapplication (this command is intended to be run on the fvp-model via theterminal_uart_apwindow):simpleperf record -e cs-etm program
More info on the
simpleperftool can be found here.convert the execution trace to instruction samples with branch histories;
The execution trace can be converted to an instruction profile using the
simpleperfapplication. The followingsimpleperf injectcommand will decode the execution trace and generate branch histories in text format accepted by AutoFDO (this command is intended to be run on the fvp-model via theterminal_uart_apwindow):simpleperf inject -i perf.data -o inj.data --output autofdo --binary program
convert the instruction samples to source level profiles;
The AutoFDO tool is used to convert the instruction profiles to source profiles for the
GCCandclang/llvmcompilers.This requires to pull the instruction profile (generated in the previous step and saved as
inj.datafile), from the model to the host machine using theadbcommand (please refer to the ADB - Download a file section for more info how to do this).The instruction samples produced by
simpleperf injectwill be passed to the AutoFDO tool to generate source level profiles for the compiler. The following line demonstrates the usage command forclang/llvm(this command is intended to be run on the host machine):create_llvm_prof -binary=program -profile=inj.data -out=program.llvmprof
use the source level profile with the compiler;
The profile produced by the above steps can now be provided to the compiler to optimize the next build of the
programapplication. Forclang, use the-fprofile-sample-usecompiler option as follows (this command is intended to be run on the host machine):clang -O2 -fprofile-sample-use=program.llvmprof -o program program.c
ADB connection on Android
- This section applies to Android distros and describes the steps required to use ADB protocol to perform the following actions (always considering a remote running FVP-model Android instance):
connect to a running fvp-model instance;
upload a file;
download a file;
execute a command via ADB shell.
Connect to the running FVP-model instance
run the fvp-model and wait for the instance to fully boot up (this may take a considerable amount of time depending on the distro under test and the host hardware specification);
once the Android distro boot completes (and the
Fast Models - Total Compute 2 DP0window shows the complete Android home screen), run the following commands on a new host terminal session to connect to the fvp-model running instance via theadbprotocol:
adb connect 127.0.0.1:5555 adb devicesThe following excerpt capture demonstrates the execution and expected output from the previous commands:
# adb connect 127.0.0.1:5555 * daemon not running; starting now at tcp:5037 * daemon started successfully connected to 127.0.0.1:5555 # adb devices List of devices attached 127.0.0.1:5555 offline
Note
If the previous command fails to connect, please wait a few more minutes and retry. Due to the indeterministic services boot flow nature, this may circumvent situations where the fvp-model Android instance takes a bit longer to start all the required services and correctly allow communications to happen.
Warning
If running more than one FVP-model on the same host, each instance will get a different ADB port assigned. The assigned ADB port is mentioned during the FVP-model start up phase. Please ensure you are using the correct assigned/mentioned ADB port and adapt the commands mentioned in this entire section as needed (i.e. replacing default port 5555 or <fvp adb port> mentions with the correct port being used).
Upload a file
connect or ensure that an ADB connection to the fvp-model is established;
run the following command to upload a local file to the remote fvp-model Android running instance:
adb -s <fvp adb port> push <local host location for original file> <remote absolute path location to save file>
Note
It may happen that the ADB connection is lost between the connection moment and the moment that the previous command is run. If that happens, please repeat the connection step and the previous command.
Download a file
connect or ensure that an ADB connection to the fvp-model is established;
run the following command to download a remote file to your local host system:
adb -s <fvp adb port> pull <remote absolute path location for original file> <local host location where to save file>
Note
It may happen that the ADB connection is lost between the connection moment and the moment that the previous command is run. If that happens, please repeat the connection step and the previous command.
Execute a remote command
adb -s <fvp adb port> shell <command>
Example:
adb -s <fvp adb port> shell ls -la
Note
It may happen that the ADB connection is lost between the connection moment and the moment that the previous command is run. If that happens, please repeat the connection step and the previous command.
Set up TAP interface for Android ADB
This section applies to Android and details the steps required to set up the tap interface on the host for model networking for ADB.
The following method relies on libvirt handling the network bridge. This solution provides a safer approach in which, in cases where a bad configuration is used, the primary network interface should continue operational.
Steps to set up the tap interface
To set up the tap interface, please follow the next steps (unless otherwise mentioned, all commands are intended to be run on the host system):
install
libvirton your development host system:sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install libvirt-daemon-system libvirt-clients
The host system should now list a new interface with a name similar to
virbr0and an IP address of192.168.122.1. This can be verified by running the commandifconfig -a(or alternativelyip a sfor newer distributions) which will produce an output similar to the following:$ ifconfig -a virbr0: flags=4099<UP,BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 inet 192.168.122.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.122.255 ether XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 virbr0-nic: flags=4098<BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 ether XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 $
create the
tap0interface:sudo ip tuntap add dev tap0 mode tap user $(whoami) sudo ifconfig tap0 0.0.0.0 promisc up sudo brctl addif virbr0 tap0
download and install the Android SDK from here or, alternatively, install the
adbtool package as follows:sudo apt-get install adb
run the FVP model providing the additional parameter
-t "tap0"to enable the tap interface:./run-scripts/tc2/run_model.sh -m <model binary path> -d android-fvp -t "tap0"
Before proceeding, please allow Android FVP model to fully boot and the Android home screen display to be visible on the
Fast Models - Total Compute 2 DP0window.Note
Running and booting the Android FVP model will take considerable time, potentially taking easily 2-3+ hours depending on your host system hardware specification. Please grab a coffee and relax.
once the Android FVP model boots, the Android instance should get an IP address similar to
192.168.122.62, as illustrated in the next figure: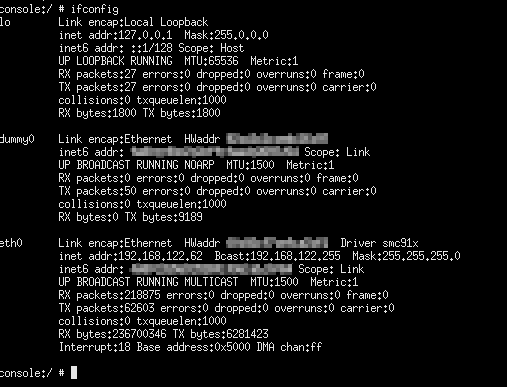
validate the connection between the host
tap0interface and the Android FVP model by running the following command on the fvp-model via theterminal_uart_apwindow:ping 192.168.122.1
Alternatively, it is also possible to validate if the fvp-model can reach a valid internet gateway by pinging, for instance, the IP address
8.8.8.8instead.at this stage, you should also be able to establish an ADB connection and upload/download files as described in section ADB connection on Android.
Steps to graceful disable and remove the tap interface
To revert the configuration of your host system (removing the tap0 interface), please follow the next steps:
remove the
tap0from the bridge configuration:sudo brctl delif virbr0 tap0
disable the bridge interface:
sudo ip link set virbr0 down
remove the bridge interface:
sudo brctl delbr virbr0
remove the
libvirtpackage:sudo apt-get remove libvirt-daemon-system libvirt-clients
Copyright (c) 2022-2023, Arm Limited. All rights reserved.